In a world marked by rapid technological evolution and unpredictable market dynamics, businesses must remain nimble to survive and thrive. To navigate this complex landscape, many organizations are embracing Agile and Lean methodologies.
Originating from the software development and manufacturing sectors respectively, these philosophies have revolutionized the way organizations operate, fostering innovation, enhancing customer satisfaction, and improving operational efficiency.
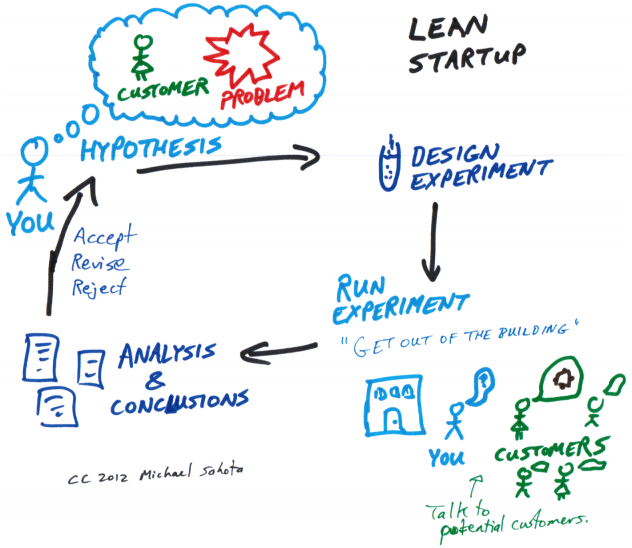
Understanding Agile and Lean
Agile methodology, birthed in the software development world, is a project management and product development approach that encourages flexibility, collaboration, and customer-centricity.

It values individuals and interactions over processes and tools, working products over comprehensive documentation, customer collaboration over contract negotiation, and responding to change over following a plan.
On the other hand, Lean methodology, which originated from Toyota’s production system, focuses on maximizing customer value while minimizing waste. In simpler terms, Lean means creating more value for customers with fewer resources. It emphasizes continuous improvement, efficiency, and quality.
Agile and Lean in Modern Management
These methodologies have transcended their original domains, proving valuable across various sectors and management functions. Businesses today operate in a VUCA (volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous) environment.
In this setting, the ability to swiftly adapt to changes is a competitive advantage. Agile and Lean methodologies equip organizations with this adaptability.
Agile management promotes a decentralized decision-making structure, empowering employees to make decisions based on real-time data. This approach encourages innovation, enhances speed, and facilitates swift response to changes.
Lean management, meanwhile, fosters efficiency by eliminating waste and optimizing processes. This not only reduces costs but also improves quality and speeds up delivery. Lean’s emphasis on continuous improvement creates a culture of excellence where employees consistently strive to enhance their performance.
The Synergy of Agile and Lean
While Agile and Lean methodologies have distinct origins and principles, they share commonalities and can be synergistically applied. Both methodologies focus on delivering value to the customer, promote continuous improvement, and advocate for waste elimination.
The combination of Agile and Lean can create a potent management approach. Agile’s flexibility and customer-centricity, coupled with Lean’s efficiency and waste reduction, can lead to high-quality outputs delivered promptly and cost-effectively.
In an Agile-Lean environment, teams work in iterative cycles, learning from each step, incorporating feedback, and continuously improving. This approach allows organizations to quickly adjust to changing customer needs, market dynamics, or operational challenges.

As we delve deeper into this topic, we’ll explore how organizations can implement Agile and Lean methodologies, the challenges they might face, and the potential benefits to be reaped.
Implementing Agile and Lean Methodologies
Integrating Agile and Lean methodologies into an organization’s operations requires a significant cultural shift and the willingness to embrace change at all levels. To start, management should define clear objectives aligned with customer needs and organizational goals.
These objectives guide the implementation and provide a benchmark to measure progress.
Agile implementation often starts with selecting an Agile framework, such as Scrum or Kanban. These frameworks provide structures for iterative work cycles, known as ‘sprints’ in Scrum, which allow teams to develop, test, and improve products or services in small increments.
Teams self-organize, make decisions collaboratively, and continually refine their work processes based on feedback and lessons learned.
Lean implementation, on the other hand, involves identifying and eliminating waste in all business processes. ‘Waste’ in Lean parlance refers to anything that doesn’t add value for the customer.
This could be wasted time, materials, or effort. Lean tools such as value stream mapping, 5S, and Kaizen can be invaluable in spotting waste and identifying improvement opportunities. Lean also promotes ‘pull’ systems, where production is driven by customer demand, minimizing inventory costs and reducing lead time.
Challenges in Agile and Lean Implementation
Implementing Agile and Lean methodologies is not without challenges. One common hurdle is resistance to change. Employees accustomed to traditional management approaches might find Agile and Lean practices disruptive or intimidating.
Overcoming this resistance requires strong leadership, clear communication, and possibly, training sessions to help staff understand and embrace the new methodologies.

Organizations might also grapple with the lack of immediate results. Both Agile and Lean are long-term strategies, and it may take time before the benefits become evident. Patience, persistence, and a focus on incremental improvements are crucial during this transition period.
The Potential Benefits of Agile and Lean Methodologies
Despite these challenges, the benefits of implementing Agile and Lean methodologies can be substantial. From a management perspective, these methodologies foster a culture of collaboration, innovation, and continuous improvement.
They empower employees to make decisions, promoting accountability and enhancing job satisfaction.
From a business perspective, Agile and Lean methodologies can improve productivity, quality, and customer satisfaction. Agile’s iterative approach allows organizations to deliver value to customers quickly and incorporate feedback promptly, enhancing the product-market fit. Lean, with its focus on efficiency and waste reduction, can lead to significant cost savings and quality improvements.
Real-World Applications of Agile and Lean
Numerous organizations across sectors have adopted Agile and Lean methodologies with significant success. For example, Spotify, the popular music streaming service, has integrated Agile principles into its organizational structure.
The company operates in squads (small cross-functional teams), tribes (groups of squads), chapters, and guilds, promoting autonomy, mastery, and purpose. This Agile structure has enabled Spotify to innovate rapidly and adapt to changing user demands.
Toyota, the birthplace of Lean, is another noteworthy example. The company’s manufacturing system, with its focus on continuous improvement (Kaizen) and waste elimination, has served as a model for organizations worldwide.
Toyota’s success story demonstrates how Lean principles can drive efficiency, quality, and customer satisfaction.
Strategies for Successful Implementation
Effective implementation of Agile and Lean methodologies requires careful planning, clear communication, and strong leadership. Here are some strategies for success:
Leadership Commitment
Leaders must fully understand and commit to Agile and Lean principles. They should model these behaviors and promote a culture of flexibility, continuous improvement, and customer-centricity.
Training and Education
Investing in training programs can help employees understand and apply Agile and Lean principles. This also demonstrates the organization’s commitment to these methodologies, fostering employee buy-in.
Gradual Implementation
Start small and gradually scale up. Implementing Agile or Lean in one project or department allows the organization to learn from experience and refine the approach before wider implementation.
Regular Reflection
Regular retrospectives can help teams reflect on what’s working and what’s not, enabling continuous improvement.
Conclusion: The Agile-Lean Future of Management
In today’s fast-paced, unpredictable business environment, Agile and Lean methodologies are more relevant than ever. These methodologies empower organizations to respond swiftly to changes, innovate continuously, and deliver maximum value to customers.
While implementing Agile and Lean methodologies can be challenging, the potential benefits — improved efficiency, quality, customer satisfaction, and employee engagement — are significant. As more organizations recognize these benefits, Agile and Lean are likely to continue shaping the future of management.
Through ongoing commitment, patience, and learning, businesses can harness the power of Agile and Lean, fostering a culture of adaptability, innovation, and excellence. The journey may be complex, but the destination — a nimble, customer-centric organization primed for success in the modern business landscape — is well worth the effort.

